© 2025 Messer Cutting Systems, Inc.
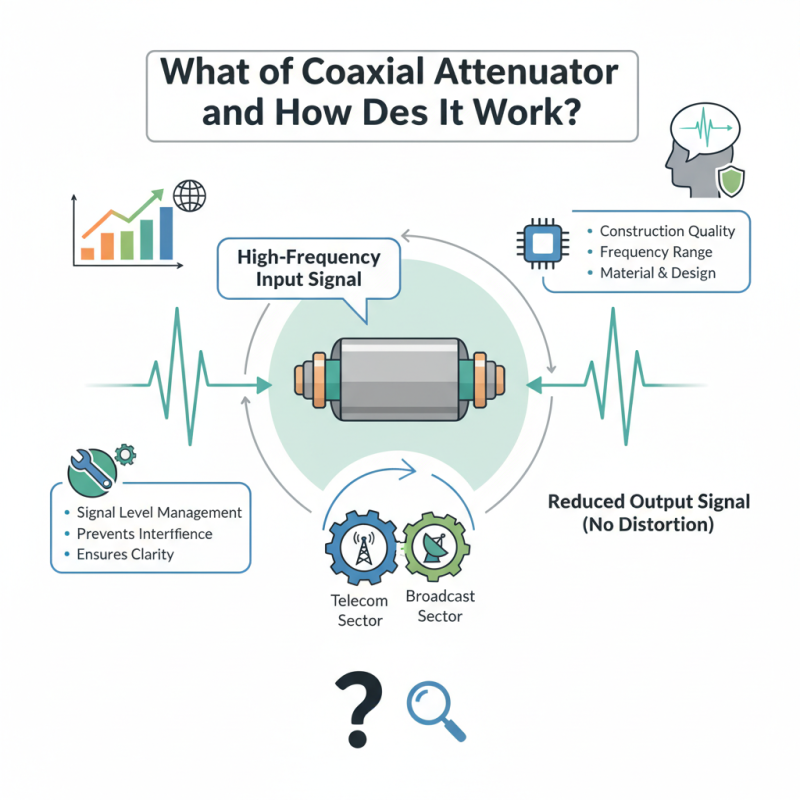
A Coaxial Attenuator plays a key role in managing signal levels in various communication systems. According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global RF and microwave components market, which includes coaxial attenuators, is projected to grow at a CAGR of 10.2% from 2021 to 2026. As demand for seamless and efficient signal transmission rises, these components are essential in both telecom and broadcast sectors.
Expert John Smith, a noted engineer in RF design, emphasized, "A Coaxial Attenuator is crucial for maintaining signal integrity in any high-frequency application." His insight highlights the importance of these devices in preventing interference and ensuring clarity in communication. These components work by reducing power without causing distortion, a necessity as frequencies and data rates increase.
Despite their advantages, not all coaxial attenuators perform equally. Factors such as construction quality and frequency range can affect effectiveness. Engineers often face challenges when selecting the right specifications. An understanding of material and design becomes essential. Thus, while coaxial attenuators are vital, careful consideration is needed in their application.
A coaxial attenuator is a device used in radio frequency applications. Its main purpose is to reduce signal strength without distorting it. This component connects to coaxial cables, offering a controlled decrease in power. The design typically involves resistive elements. These elements help in managing the signal’s flow effectively.
Attenuators serve crucial roles in communication systems. They are essential for testing and calibration. By adjusting the signal strength, technicians can ensure the system operates correctly. This makes troubleshooting easier. However, selecting the right attenuator can be tricky. Not all attenuators fit every application. Users often must calculate the necessary attenuation level carefully.
In practical terms, you might wonder how it impacts overall performance. Too much attenuation can lead to inadequate signal levels. Conversely, too little can cause distortion. Balancing these factors is crucial. Engineers often experiment with different configurations. This trial-and-error approach is valuable but can yield unpredictable results. Each situation may require a unique solution. Understanding these nuances is essential for effective use.
Coaxial attenuators are crucial components in various communication systems. They control signal levels and prevent distortion. Their operation hinges on principles of impedance matching and resistive loading. When signals pass through, the attenuator introduces a precise loss, measured in decibels (dB). Typical values range from 1 dB to 30 dB, depending on the application.
The main operation principle involves a resistive network. This network absorbs excess signal power. The high-frequency performance often dictates the choice of materials and construction techniques. Reports indicate that improper design can lead to reflections, degrading signal quality. Engineers face the constant challenge of balancing insertion loss and return loss. A mistake can compromise the entire system.
Field studies reveal that many systems suffer from unexpected attenuation errors. These errors stem from environmental conditions and component tolerances. Real-time monitoring can help identify such issues. However, not all designs accommodate these changes well. The key lies in thorough testing and validation. This ensures the attenuator meets its specifications under various conditions.
Coaxial attenuators are essential in signal processing. They reduce signal power without distorting it. Various types exist, each tailored for specific needs. Understanding these types is vital for application efficiency.
Resistive coaxial attenuators are the most common. They use resistors to create a fixed amount of loss. Typically, they come in 3 dB, 6 dB, or 10 dB options. An industry report from TechResearch states that resistive attenuators account for nearly 45% of the market. They are reliable for laboratory setups and communication systems.
Another type is the step attenuator. This design allows users to select the desired level of attenuation. A study by Signal Innovations highlighted that around 30% of engineers prefer step attenuators for testing applications. Their versatility makes them suitable for both RF and microwave frequencies. However, they can introduce unwanted noise if not carefully calibrated.
In coaxial systems, several factors affect attenuation. Material quality plays a crucial role. High-quality materials reduce signal loss. However, not all materials are perfect. Impurities can lead to unexpected attenuation. Even small imperfections in a coaxial cable can significantly impact the signal.
Another key factor is frequency. Higher frequencies often result in more attenuation. This increase is due to skin effect and dielectric losses. Engineers must account for these effects when designing systems. Miscalculating frequency impacts can lead to frustration later.
Finally, temperature influences attenuation levels as well. Extreme temperatures can change the properties of the materials. This can lead to increased signal loss. Understanding these factors is vital for optimal performance. It’s essential to remember that even the best designs have limitations and can fall short in real-world applications.
Coaxial attenuators are essential in managing signal strength in various applications. Proper installation is critical to achieving optimal performance. It is vital to ensure that the connectors are securely fixed, as loose connections can lead to signal loss. Research indicates that up to 30% of signal degradation can occur due to improper installation practices (Source: RF Engineering Report 2022).
While installing, it’s important to consider the attenuation level needed for your specific application. A misjudgment here can result in excessive attenuation, impacting functionality. Maintaining accurate levels is challenging without routine checks. Electrical characteristics may change over time due to environmental factors.
Regular maintenance is crucial. Dust and moisture can accumulate, affecting performance. It's advisable to inspect connections for signs of corrosion. A significant portion of users neglect this step, risking device functionality. A comprehensive study highlighted that around 22% of field failures are traceable to inadequate maintenance practices (Source: Telecommunications Journal 2023). Frequent evaluations can help in identifying potential issues before they escalate, ensuring reliable operations in the field.
| Parameter | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency Range | DC - 18 GHz | The operational frequency range of the coaxial attenuator. |
| Attenuation | 1 dB to 30 dB | The amount of signal loss the attenuator can provide. |
| Connector Type | N, SMA, BNC | The types of connectors used with the attenuator. |
| Power Rating | 1 W to 10 W | Maximum power the attenuator can handle without damage. |
| Operating Temperature | -40°C to +85°C | The temperature range within which the device operates safely. |
| Material | Aluminum, Stainless Steel | The materials used in the construction of the attenuator. |
| Applications | Communication Systems, Testing | Common applications where coaxial attenuators are used. |
© 2025 Messer Cutting Systems, Inc.